One Important Auto Part
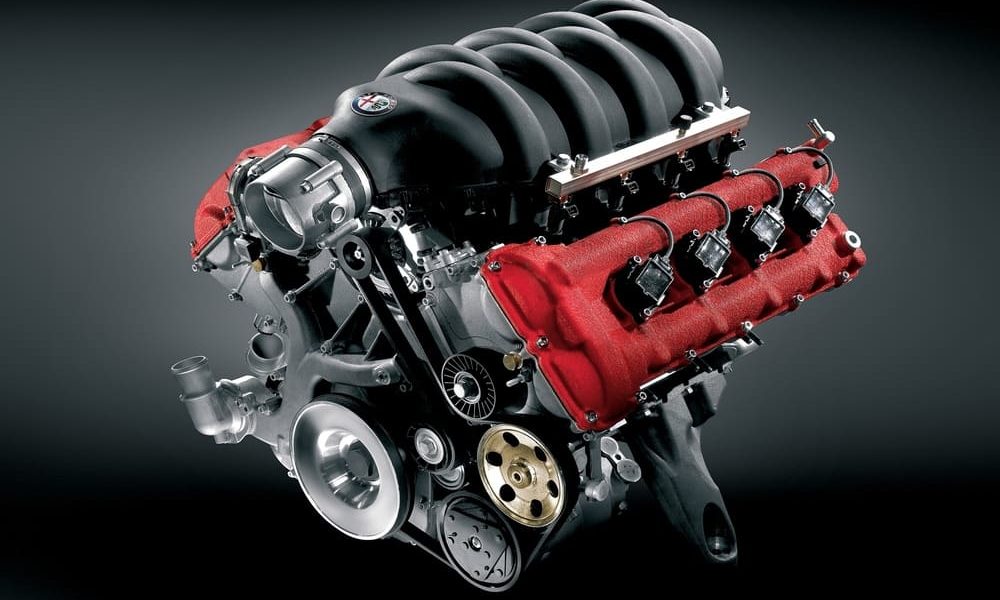
One of the most important auto parts in your vehicle is the engine. Although a highly intricate and complex mechanism, understanding the basics of how your car’s engine works doesn’t have to be so hard. Simply put, the point of your car’s engine is to take fuel—i.e. gasoline—and convert that fuel into motion. The gasoline is burned internally, which is where the name “internal combustion engine” comes from. It then emits exhaust and emissions. Of course there are several types of engines that vary in how they operate and what types of fuel they use, but we will focus on the basics.
How Internal Combustion Works
When fuel is ignited in a small, enclosed space, gas expands to create a blast of energy. In an engine, the energy created from internal combustion moves small devices called pistons which are located in an engine’s cylinders. Cylinders are the enclosures within an engine in which pistons move up and down. Generally speaking, the higher number of cylinders in an engine, the more power is created because more pistons are working to create energy. These pistons turn another device called a crankshaft which creates circular motion.
Multi-Cylinder Engines
There are a number of different configurations and cylinder quantities that have their own unique pros and cons. Depending on the arrangement, an engine may perform better, cost less to manufacture, or be shaped differently. More often than not, cars have either 4, 6, or 8 cylinders. Some are arranged in line with each other, some are flat, and some are in a “V” shape. There are some perfectly efficient four-cylinder engines just as there are less efficient eight-cylinder engines.
How Your Engine Starts
Turning your car key causes a motor to spin which starts the combustion process. This motor is very powerful and requires a lot of electricity to get going. A large electronic device called a solenoid helps generate the power needed to spin the motor and begin combustion.
Engine Cooling
Your car’s engine needs to be cooled by either water which circulates around the cylinders and through a radiator or by air which flows through an air filter and directly into the cylinders. Air needs to be circulated through the engine, and is sometimes pressurized in high-performance engines.
Courtesy of aeroautoparts